Table of Contents
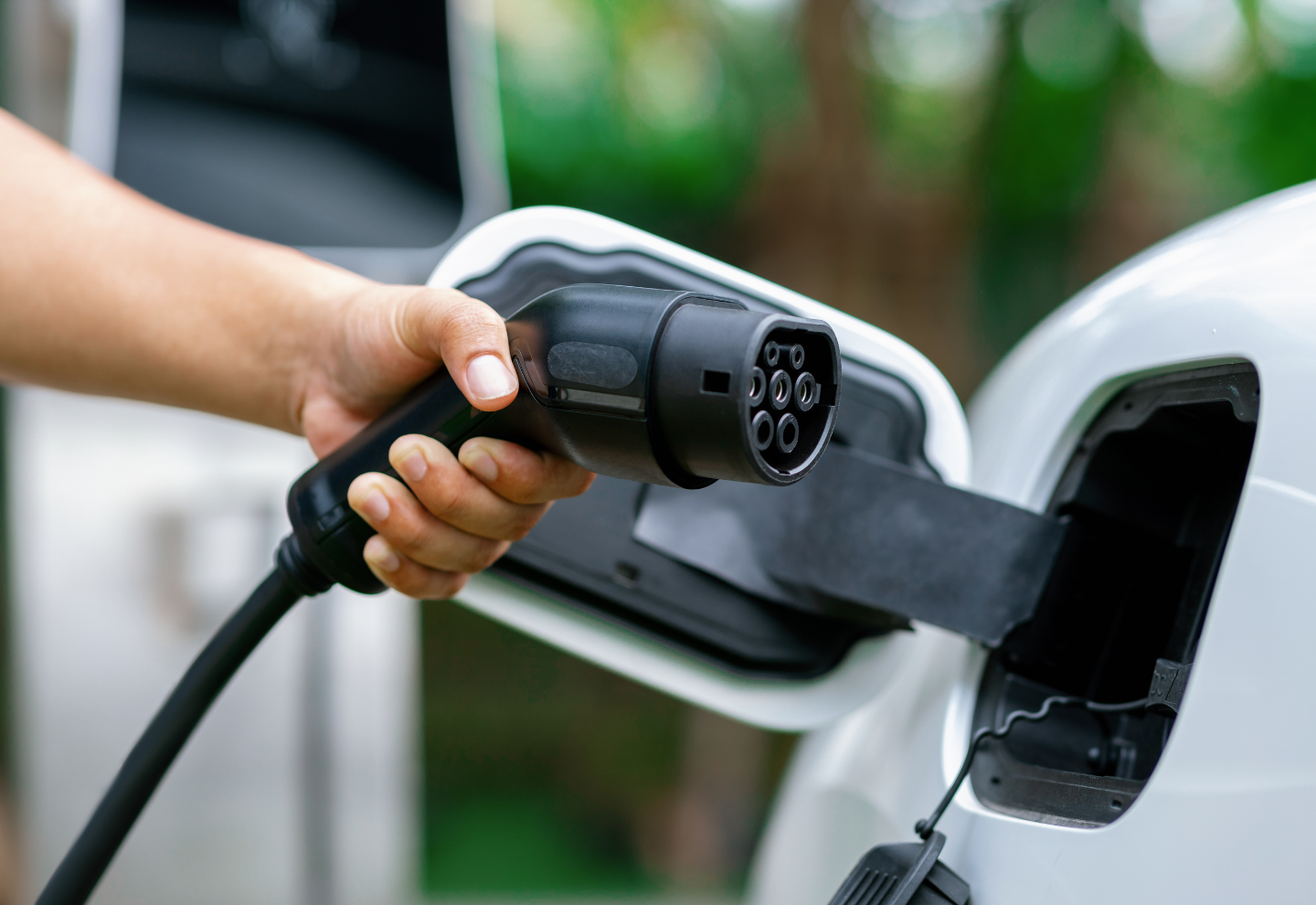
As electric vehicle (EV) ownership continues to grow rapidly across the United Kingdom, more homeowners are turning to domestic EV charging solutions. One of the most critical components of a safe and efficient home charging setup is selecting the correct cable size.
This guide explores what size cable for electric car charger UK homeowners should choose, taking into account technical specifications, regulatory standards, safety considerations, and installation best practices.
Understanding EV Charging Types in the UK
Before determining the correct cable size, it is important to understand the different levels of EV charging typically available in residential settings:
Level 1: Slow Charging (Up to 3 kW)
Slow chargers use a standard 13A plug socket and can take 10–12 hours or more to fully charge an EV. These are typically used as a backup option and not ideal for regular home charging.
Level 2: Fast Charging (7 kW – 22 kW)
These are the most common home chargers in the UK. A 7.4 kW charger running on a 230V supply with a 32A current is generally sufficient for overnight charging and is compatible with most EVs.
Level 3: Rapid Charging (43 kW and above)
Rapid chargers are found at public charging stations and are not suitable for home installations due to their high power demands and three-phase requirements.
What Size Cable for Electric Car Charger UK Installations?
The search query what size cable for electric car charger UK highlights a crucial concern among EV owners: selecting the appropriate cable gauge for safety, efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
For most residential 7 kW EV chargers operating at 230V with a 32A current, the following cable sizes are recommended:
| Cable Size (mm²) | Maximum Recommended Run Length | Use Case |
| 6 mm² | Up to 15 metres | Standard installations |
| 10 mm² | 15–30 metres | Longer runs, future-proofing |
| 16 mm² | 30+ metres | Rare in domestic installs, long-distance or higher loads |
Always consult a qualified electrician to confirm calculations specific to your installation site.
Key Factors That Influence Cable Sizing
Several factors must be considered when selecting cable size for an electric vehicle charging installation:
1. Current Load (Amperage)
Most 7 kW home chargers draw a continuous 32A current. The cable must be able to carry this load without overheating.
2. Voltage
UK homes typically operate at a single-phase 230V supply. Voltage affects the power delivered and contributes to voltage drop calculations.
3. Cable Run Length
Longer distances increase resistance, leading to voltage drop. To mitigate this, thicker cables are needed for longer cable runs.
4. Installation Environment
Cables run through insulation, ducting, or buried underground may require derating due to increased heat retention or exposure to moisture.
5. Material and Type
Copper is the standard conductor material. For outdoor installations, Steel Wire Armoured (SWA) cable is recommended. For indoor use, Twin and Earth may be suitable.
UK Regulations and Compliance
When installing an EV charger, it is essential to comply with UK wiring standards, including:
- BS 7671 (IET Wiring Regulations)
- Part P of the Building Regulations
- The Electricity at Work Regulations 1989
A dedicated radial circuit with an RCBO or Type A RCD must be installed. The charger should also have PEN fault protection if connected to a PME (Protective Multiple Earthing) system, as per current guidance.
Safety Considerations for Domestic Installations
Choosing an undersized cable can lead to serious consequences including:
- Overheating or fire
- Insulation damage
- Reduced charger lifespan
- Non-compliance with legal standards
Safety Recommendations:
- Use a minimum 6 mm² cable for 7 kW installations up to 15 metres.
- Increase to 10 mm² for longer distances to maintain acceptable voltage drop (typically less than 5%).
- For outdoor installations, use SWA cable to protect against physical and environmental damage.
- Avoid routing cables through thermal insulation unless adjusted for heat derating.
Installation Guidelines for UK Homeowners
1. Pre-Installation Survey
A qualified electrician should perform a full load assessment of your property, evaluating fuse board capacity, main supply rating, and existing circuits.
2. Circuit Protection
Install a dedicated circuit with a suitable protective device (e.g. 32A MCB or RCBO) in the consumer unit. Surge protection and PEN fault detection are also recommended.
3. Cable Routing
Plan a route that avoids unnecessary bends, sharp edges, or exposure to high temperatures or moisture. Where cables are buried, ensure proper depth and mechanical protection.
4. Earthing and Bonding
Proper earthing arrangements must be in place. If PME is present, consider using a charger with built-in open PEN conductor protection or install a TT earthing system.
5. Testing and Certification
Upon completion, your electrician must issue an Electrical Installation Certificate (EIC) and notify building control under Part P requirements.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When choosing a cable size for EV charging, avoid these common errors:
- Using the smallest possible cable size to cut costs—this often leads to overheating and regulatory issues.
- Underestimating cable length and neglecting voltage drop.
- DIY installations—only certified professionals should carry out EV charger installations.
- Incorrect earthing configuration, especially on PME systems.
- Overlooking thermal derating when cables are routed through insulation.
Practical Example
Scenario:
You’re installing a 7.4 kW wall-mounted charger in a garage located 25 metres from your home’s consumer unit.
Solution:
A 10 mm² SWA cable is recommended to handle the 32A load over that distance while minimizing voltage drop. The cable should be installed on a dedicated circuit, protected by a 32A RCBO, with earthing and bonding fully compliant with BS 7671 standards.
Final Recommendations for EV Owners in the UK
To summarise, choosing what size cable for electric car charger UK homes require involves more than simply checking amperage ratings. It demands careful evaluation of current, voltage, distance, installation conditions, and compliance with regulations.
Key Takeaways:
- For most 7 kW chargers:
→ Use 6 mm² cable for runs up to 15 metres
→ Use 10 mm² cable for runs between 15 and 30 metres - Always calculate voltage drop and follow BS 7671 standards.
- Hire a qualified, OZEV-registered electrician.
- Choose durable cable types like SWA for outdoor use.
- Consider future-proofing your installation by upsizing the cable slightly.
Making informed choices ensures not only the safety of your home but also the long-term performance and reliability of your EV charging system.