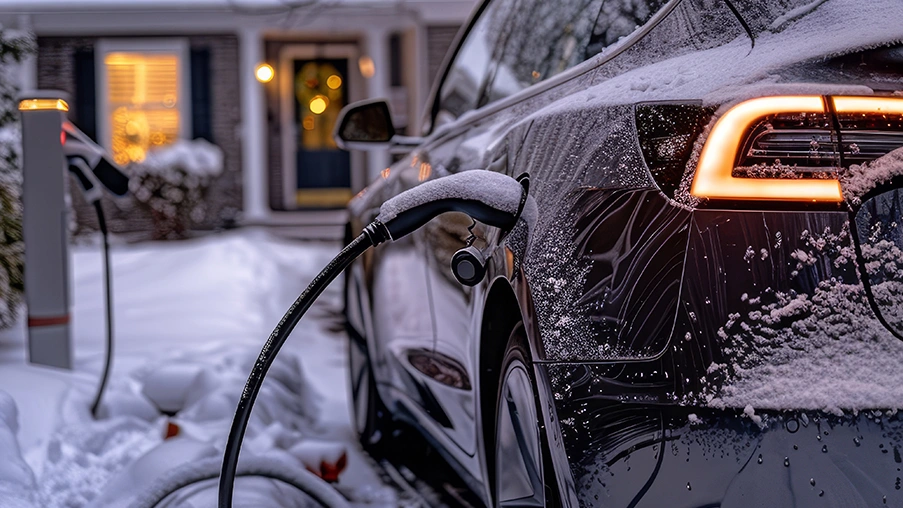
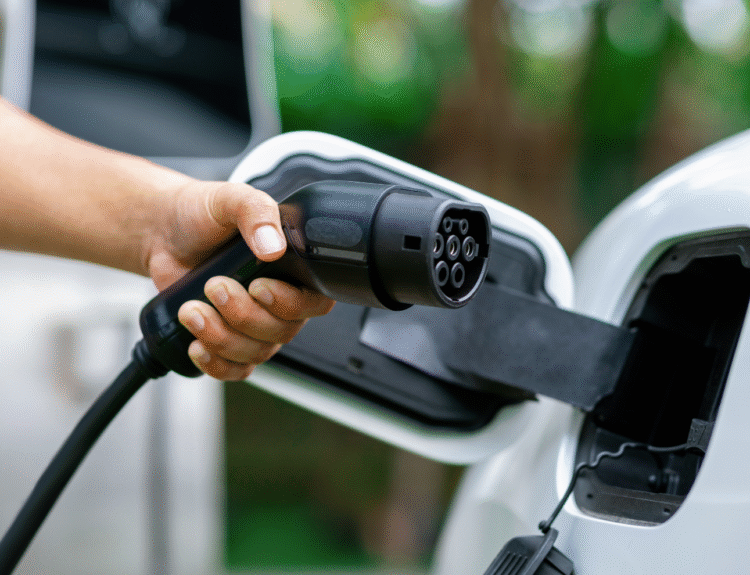
As electric vehicles (EVs) gain popularity across colder regions, many owners are asking a vital question: how to winterize an electric car to maintain peak performance in freezing temperatures? Cold weather poses unique challenges for EVs, particularly affecting battery range, efficiency, and driving safety. This comprehensive guide outlines practical and effective steps to prepare your electric car for winter, ensuring reliable and optimized performance all season long.
Why Winter Impacts Electric Vehicles Differently
Unlike internal combustion engine vehicles, EVs rely on lithium-ion batteries that are highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Cold temperatures reduce battery efficiency, extend charging times, and limit driving range. Furthermore, auxiliary systems like cabin heaters draw significant power from the battery, compounding energy loss.
Winterizing an electric car means taking strategic steps to mitigate these impacts—ensuring not only comfort and efficiency but also safety and long-term battery health.
1. Optimize Battery Performance in Cold Temperatures
The battery is the heart of your EV, and its performance can drop by 20–40% in cold conditions. Here’s how to protect and maintain its efficiency:
Precondition the Battery
Use your vehicle’s preconditioning feature to warm up the battery while it’s still plugged in. This reduces strain during the first miles of driving and helps preserve range.
Charge Smartly
Schedule your EV to finish charging right before your morning departure. A warm, fully charged battery performs significantly better than one left idle overnight.
Maintain an Optimal State of Charge
Avoid letting the battery drop below 20% or stay at 100% for extended periods in winter. Aim to keep it between 20%–80% for optimal battery health.
Park Indoors When Possible
Whenever feasible, park your EV in a garage to reduce exposure to freezing temperatures. If indoor parking isn’t available, invest in a quality, insulated car cover to minimize battery cooling overnight.
2. Use the Right Tires for Winter Conditions
Tires play a vital role in EV efficiency and safety. Cold temperatures harden summer or all-season tires, reducing grip and increasing braking distance.
Install Winter Tires
Winter tires are specifically designed for snow, ice, and sub-zero temperatures. Their softer rubber compound and aggressive tread patterns enhance traction and safety.
Maintain Proper Tire Pressure
Cold air reduces tire pressure, which can affect efficiency and range. Check and inflate your tires regularly, keeping them within the manufacturer’s recommended PSI.
3. Improve Charging Strategy for Cold Weather
Charging can be slower in the winter due to battery temperature and decreased chemical reactivity. Implement these strategies:
Use Level 2 Charging at Home
Faster than a regular wall outlet, a Level 2 charger allows for more efficient overnight charging and supports preconditioning.
Avoid Fast Charging When the Battery Is Cold
Fast charging a cold battery can lead to lithium plating and long-term battery damage. Warm the battery through preconditioning or driving before using DC fast charging stations.
Monitor Charging Cables and Ports
Ice and snow can obstruct charging port lids and connectors. Clean and dry these components before and after charging to avoid corrosion or mechanical failure.
4. Maximize Cabin Efficiency and Comfort
Heating the cabin draws heavily on your EV’s battery, affecting range. Implement these measures to stay warm without sacrificing efficiency:
Use Heated Seats and Steering Wheel
These consume less energy than cabin heaters. Use them as your primary heat sources when possible.
Dress for the Weather
Wearing warm clothing reduces reliance on the cabin heater, preserving battery life for driving needs.
Reduce HVAC Use
Set the climate control to a lower temperature and use eco mode if available. This balances comfort and range conservation.
5. Update Software and Inspect EV Systems
Regular software updates often include optimizations for winter performance. Additionally, general maintenance ensures that your EV is prepared for harsh conditions.
Check for Software Updates
Manufacturers regularly release updates that enhance thermal management and charging algorithms. Always install the latest firmware before winter.
Inspect Battery Coolant and HVAC System
A technician should check your thermal management systems to ensure the battery and cabin heating systems function correctly.
Test Wiper Blades and Washer Fluid
Use winter-grade washer fluid and replace worn blades to maintain clear visibility in snow and slush.
6. Plan Winter Trips with Charging in Mind
In winter, range can be unpredictable. Always plan your trips with extra buffer distance and consider alternative charging locations.
Use EV Navigation Tools
Most EVs and apps like PlugShare or A Better Routeplanner (ABRP) allow you to map routes with charging stops, taking temperature and elevation into account.
Carry an Emergency Kit
Pack a winter emergency kit that includes a portable charger, blankets, power bank, flashlight, shovel, and tire chains—especially for rural or snowy areas.
7. Drive Efficiently in Winter Conditions
How you drive impacts your battery just as much as external conditions. Adjusting your driving habits during winter can preserve range and enhance safety.
Accelerate Smoothly and Decelerate Gradually
Avoid sudden starts and stops that demand high power and reduce regenerative braking effectiveness in icy conditions.
Use Regenerative Braking Wisely
While helpful, regenerative braking may behave unpredictably on slick roads. Lower the regen setting if your vehicle allows, and use manual braking when necessary.
Reduce Speed
Driving at lower speeds conserves energy and increases range—especially important when your battery’s range is already diminished.
Final Thoughts: How to Winterize an Electric Car
Understanding how to winterize an electric car is key to maximizing your EV’s performance, safety, and longevity in cold climates. By following these expert-backed tips—focusing on battery health, smart charging, appropriate tires, and efficient driving habits—you can confidently face the challenges of winter driving.
As EV adoption continues to grow, preparation and awareness are essential for enjoying the full benefits of electric mobility year-round. Stay ahead of the weather, and your EV will remain a reliable, eco-friendly companion no matter the temperature.