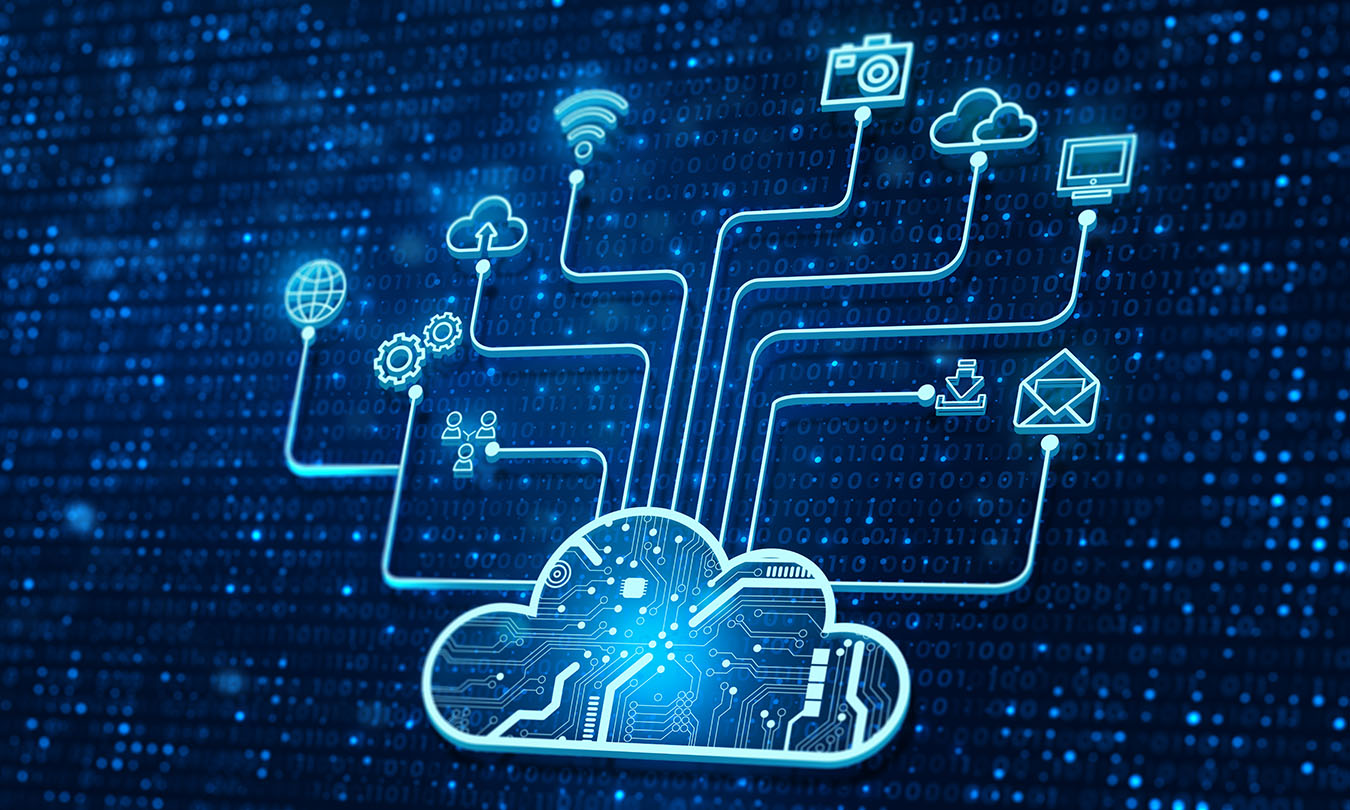
Introduction
Cloud computing has revolutionized how individuals and businesses store, manage, and access data and applications. Despite its widespread adoption, many beginners find the concept of cloud computing confusing. This guide breaks down the basics, explaining what cloud computing is, how it works, and why it has become an essential technology in today’s digital world.
1. Defining Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to delivering computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the internet (“the cloud”). Instead of owning and maintaining physical hardware and software, users can access these resources on-demand from cloud providers, paying only for what they use.
2. How Cloud Computing Works
At its core, cloud computing relies on a network of remote servers hosted in data centers around the world. These servers process and store data, allowing users to access applications and files via the internet from any device. This model provides flexibility, scalability, and reduces the need for expensive local infrastructure.
3. Key Types of Cloud Services
Cloud computing is commonly divided into three service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS offers virtualized computing resources, PaaS provides platforms for developers to build applications, and SaaS delivers software applications over the internet, such as email, collaboration tools, and customer relationship management (CRM) systems.
4. Deployment Models: Public, Private, and Hybrid Clouds
Cloud services can be deployed in various ways. Public clouds are operated by third-party providers and shared across multiple users. Private clouds are exclusive environments dedicated to a single organization, offering enhanced control and security. Hybrid clouds combine both models, allowing data and applications to move between private and public clouds for greater flexibility.
5. Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers numerous advantages including cost savings, scalability, and accessibility. Organizations can avoid upfront investments in hardware and reduce maintenance costs. Cloud resources can quickly scale up or down based on demand, and users can access their data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, promoting collaboration and remote work.
6. Common Use Cases
Cloud computing supports a wide range of applications—from hosting websites and storing data to running big data analytics and powering machine learning models. Businesses use the cloud to streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and accelerate innovation. Even individuals benefit from cloud-based services like photo storage, streaming, and productivity apps.
7. Security Considerations
While cloud providers invest heavily in security, users must also adopt best practices to protect their data. This includes managing access controls, encrypting sensitive information, and understanding the shared responsibility model where both providers and users play roles in security. Proper planning helps mitigate risks associated with data breaches and unauthorized access.
8. The Future of Cloud Computing
The cloud continues to evolve with emerging trends such as edge computing, serverless architecture, and increased integration with artificial intelligence (AI). These innovations aim to make cloud services more efficient, responsive, and intelligent, expanding their role in digital transformation across industries.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has become a cornerstone of modern technology, offering flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solutions for data storage and computing power. By understanding its fundamentals, beginners can better appreciate how the cloud is shaping the future of technology and how they can leverage it in personal and professional contexts.